VASPs are the “gateways” of crypto, such as exchanges, custodians, payment processors, OTC desks, where you on-ramp, trade, transfer, and store digital assets. They’re regulated under global AML/
KYC rules (FATF), with local frameworks like EU MiCA (CASPs) and U.S. FinCEN (MSBs). Knowing how VASPs operate helps you trade safely, withdraw smoothly, and avoid compliance hiccups like failed withdrawals due to Travel Rule checks.
Learn what Virtual Asset Service Providers (VASPs) are, how they work, and what crypto traders need to know about KYC, Travel Rule checks, and compliance in 2025.
What Is a VASP (Virtual Asset Service Provider)?
A Virtual Asset Service Provider (VASP) is a business that handles cryptocurrencies on behalf of customers. According to the Financial Action Task Force (FATF), the global body that sets anti-money laundering (AML) and counter-terrorism financing (CFT) rules, VASPs fall into one or more of these categories:
1. Exchanges: Platforms where you can swap crypto for fiat like USD or EUR or trade one crypto for another, e.g., BTC for ETH.
2. Transfers: Services that move your crypto from one account or wallet to another.
3. Custody/Safekeeping: Businesses that hold your private keys and manage digital assets for you, such as custodial wallets.
4. Financial Services Around Tokens: Companies helping with initial token sales, ICOs, or other fundraising events using digital assets.
If you’ve ever used a centralized exchange (CEX) to
buy Bitcoin, relied on a custodial wallet to store coins, used an OTC desk for large trades, or paid a merchant using a crypto payment processor, those businesses are VASPs.
Why Does VASP Matter to Crypto Traders?
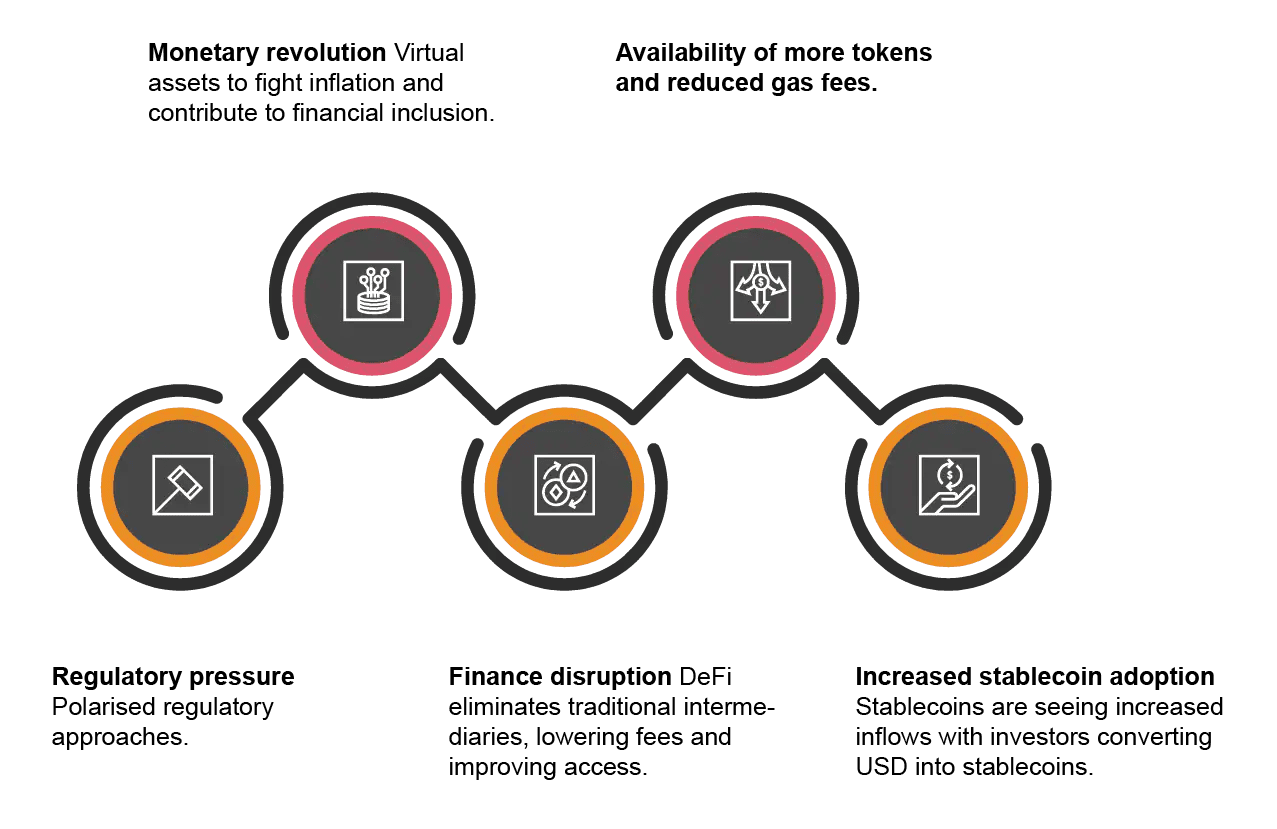
Global trends driving the growth of VASPs | Source: PwC
VASPs are the “gateways” of crypto. They’re where most users enter or exit the market, and they’re the ones regulators pay the most attention to. That’s why you’ll often be asked for KYC documents when signing up, or why withdrawals sometimes require extra verification. Understanding that exchanges and other providers are legally classified as VASPs explains why these checks exist; they’re not random, but part of global compliance rules designed to keep platforms safe and trustworthy.
What Are the Core Rules VASPs Must Follow?
Whenever you trade, deposit, or withdraw through a crypto exchange or wallet provider, you’re not just dealing with technology, you’re also interacting with compliance rules. These rules are what regulators require VASPs to follow, and they directly shape your user experience.
1. KYC / Customer Due Diligence (CDD): Almost every exchange asks for Know Your Customer (KYC) checks. At a minimum, you’ll provide your full name, date of birth, and a government-issued ID. For higher trading limits, you may need to show proof of address, like a utility bill, or even proof of income/source of funds if you’re moving large amounts. This protects platforms from money laundering risks and helps them verify that you are who you say you are.
2. Transaction Monitoring & Suspicious Activity Reports (SARs): Behind the scenes, platforms track deposits, withdrawals, and trading patterns. If a transaction looks suspicious, for example, sudden large inflows from a flagged address or coins linked to mixers, the VASP can freeze funds temporarily and may file a Suspicious Activity Report (SAR) to authorities. As a trader, this means keeping your funding sources clean and avoiding risky counterparties is crucial.
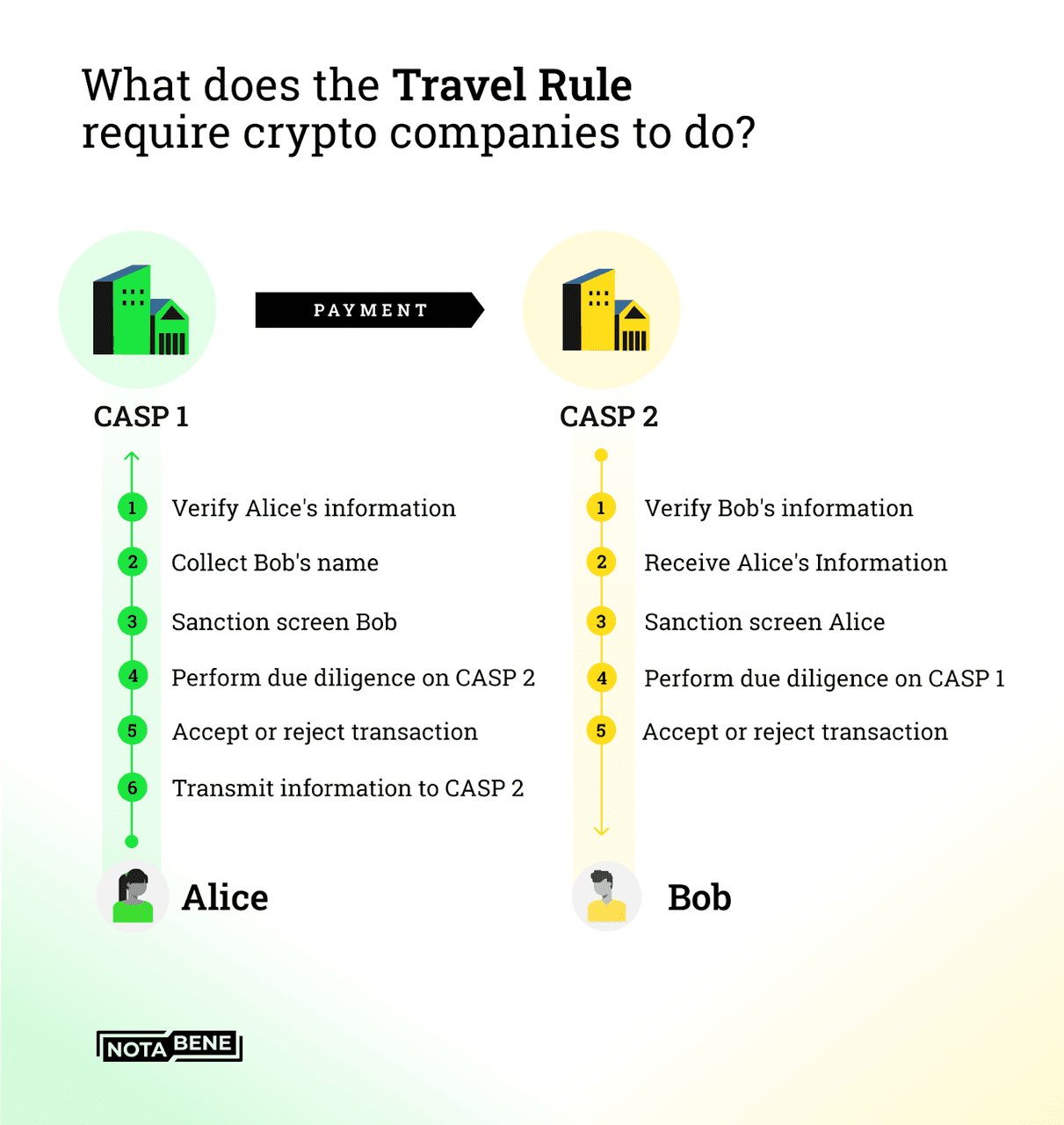
3. The Travel Rule: When you send crypto between two regulated VASPs (like Exchange A → Exchange B) and the amount is above USD/EUR 1,000, your personal details, such as name, account number, beneficiary details, must “travel” with the transaction. If this information is missing or mismatched, for example, the account name at the destination exchange doesn’t match yours, the withdrawal could be delayed, rejected, or flagged for review. This is one of the biggest reasons why withdrawals sometimes get stuck.
4. Record-Keeping: VASPs are required to keep detailed records of customer transactions for several years, commonly 5 years or more. This allows them to resolve disputes, support audits, and respond to law enforcement requests. For you, this means your transaction history is stored and may be reviewed if needed, so double-checking wallet addresses and transaction notes is always worth it.
Practical Tip: These rules exist to protect the crypto ecosystem from fraud and money laundering. The best way to avoid delays is to complete KYC early, provide accurate information, and make sure recipient details are entered exactly as required when transferring funds.
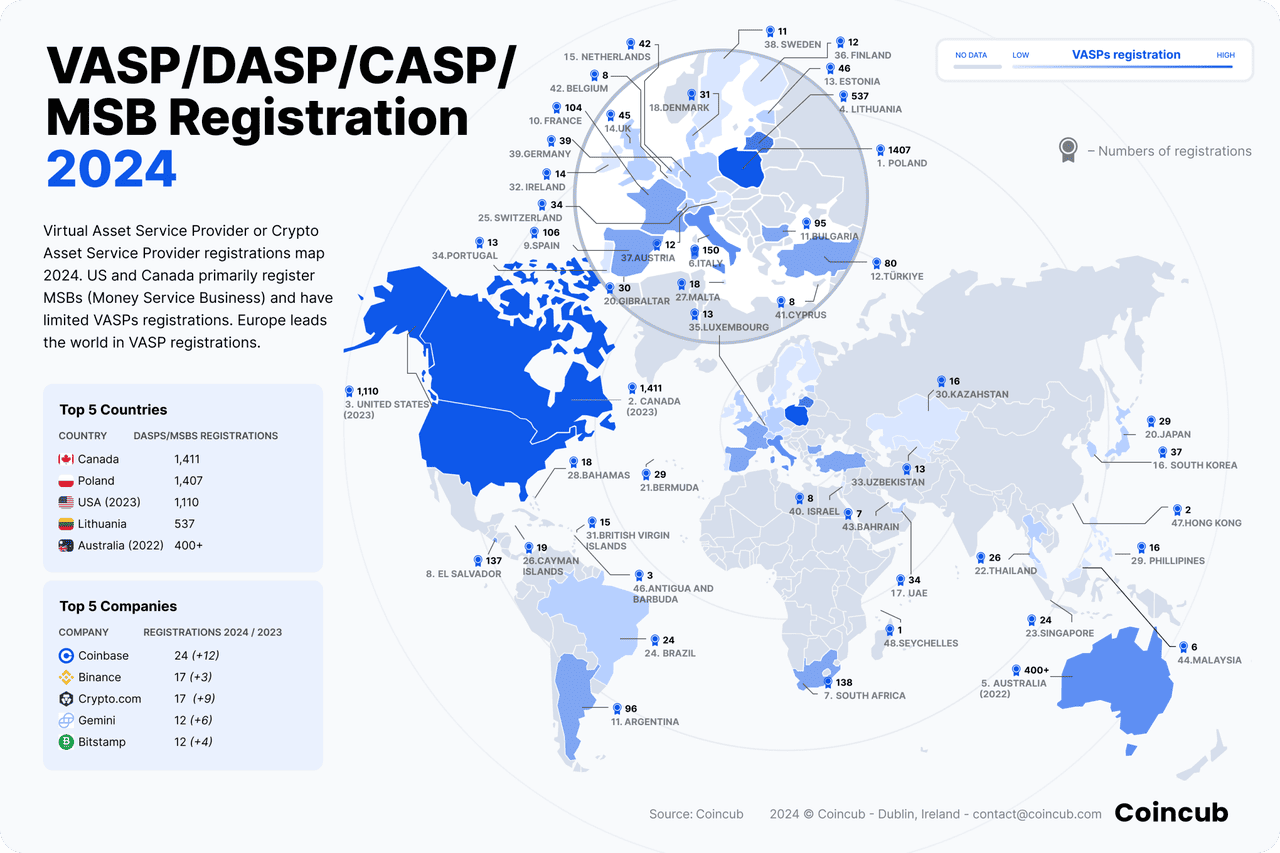
Top Rules Impacting VASPs by Geography (2025 Snapshot)
The state of VASP registration worldwide as of 2024 | Source: Coincub
Crypto compliance isn’t made up by exchanges; it comes from global standard setters and national regulators. Here’s where the main rules VASPs follow actually originate:
• Global Baseline – FATF: The Financial Action Task Force (FATF) defines what counts as a Virtual Asset (VA) and a VASP. It also created the Travel Rule, requiring customer data to accompany certain cross-border transfers. FATF doesn’t regulate companies directly; each country implements its standards in national law. This is why onboarding, withdrawal limits, and verification requirements may vary by exchange location, but the core KYC/AML rules remain universal.
• European Union – MiCA (CASPs): The EU’s Markets in Crypto-Assets Regulation (MiCA) introduces a licensed category called Crypto-Asset Service Providers (CASPs). With a CASP license, a platform can serve all 27 EU countries through “passporting.” CASPs must meet stricter requirements, such as board governance, capital reserves, risk disclosures, and user protections. From 2025–2026, the new Anti-Money Laundering Authority (AMLA) in Frankfurt will directly supervise large cross-border CASPs. For EU traders, this means smoother multi-country access, but also stricter ID checks and standardized consumer protections.
• United States – FinCEN (MSBs): In the U.S., most exchanges and custodians are treated as Money Services Businesses (MSBs) under the Bank Secrecy Act (BSA). They must register with FinCEN, run AML/KYC programs, keep records, and file Suspicious Activity Reports (SARs). Some states, like New York, add extra licensing such as the BitLicense. For U.S. traders, this results in tighter onboarding, capped withdrawal limits until verification is complete, and more frequent requests for extra documentation, especially when moving larger sums.
• United Arab Emirates – Dubai and Abu Dhabi: The UAE has built one of the world’s most advanced crypto regulatory frameworks. In Dubai, the Virtual Assets Regulatory Authority (VARA) oversees VASPs with activity-specific licenses (exchange, custody, broker-dealer, advisory). Abu Dhabi’s ADGM Financial Services Regulatory Authority runs a parallel licensing regime focused on institutional-grade compliance. Together, these frameworks position the UAE as a global hub for regulated digital assets. For traders, this means strong AML/KYC checks but also a high degree of regulatory clarity and safety.
• Other Hubs (Singapore, UK): Singapore’s Monetary Authority of Singapore (MAS) requires licenses under its Payment Services Act, while the UK’s Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) enforces registration and AML obligations. Both hubs emphasize compliance and consumer protection while promoting innovation. For traders, expect robust KYC, transaction monitoring, and clear conduct standards.
CASP vs. VASP: What’s the Difference?
A VASP (Virtual Asset Service Provider) is the global umbrella term created by the FATF. It covers any business that exchanges, transfers, or safeguards crypto on behalf of customers, like exchanges, custodial wallets, OTC desks, and payment processors. VASP rules vary by country, since each jurisdiction implements FATF standards in its own way.
A CASP (Crypto-Asset Service Provider) is the European Union’s version of a VASP, defined under the MiCA regulation. CASPs must apply for a license, follow strict governance and consumer-protection requirements, and can use “passporting” to operate across all EU member states with one approval. In short, all CASPs fit the VASP definition, but they face stricter, standardized rules in the EU, making them more heavily supervised than many VASPs elsewhere.
How a VASP Affects Your Everyday Trading
VASPs aren’t just abstract legal terms; they directly shape the way you trade, deposit, and withdraw crypto every day. Here’s how those rules show up in practice:
1. On-Ramps and Off-Ramps (KYC Tiers): When you sign up for an exchange, you’ll almost always go through KYC (Know Your Customer) checks. Basic verification, such as name, email, government ID, usually unlocks small trading and withdrawal limits, often $2,000–$5,000 per day. If you want to deposit or withdraw larger amounts, for example, $50,000+, you’ll need advanced verification like proof of address or proof of funds. This tiered system is required by regulators and helps prevent money laundering.
Example Scenario: “Why did I get asked for source of funds during a bull run?”
Rapid inflows from new banks + older coins with privacy-tool exposure → automated risk flags → extra documents requested as part of BSA/AML controls.
2. Deposits or Chain-Specific Rules: Some cryptocurrencies require extra details to process deposits correctly. For example,
XRP and
XLM deposits need a memo/tag alongside your wallet address. Forgetting it can mean your funds are delayed or lost until support intervenes. On top of that, VASPs screen incoming transactions against blockchain analytics. Coins traced back to mixers, darknet markets, or sanctioned wallets may be flagged, frozen, or rejected to stay compliant with AML laws.
3. Withdrawals Like Travel Rule and Wallet Checks: If you withdraw crypto from one VASP to another (say, Binance to Coinbase) and the amount is over USD/EUR 1,000, the sending exchange must include your details (name, account ID) with the transfer to meet the Travel Rule. If the beneficiary info doesn’t match at the receiving VASP, your withdrawal could be paused or rejected until corrected. If you’re withdrawing to a self-custody wallet, some regions (like the EU) are introducing quick “ownership checks” to confirm you control the wallet before releasing funds.
Example Scenatio: “Why did my withdrawal get stuck?”
You sent from Exchange A to Exchange B for €1,500. The beneficiary name at B didn’t match your A account details. Under the Travel Rule, A/B exchanged data, saw a mismatch, and A paused the transfer until you confirmed recipient details.
How the Travel Rule works for VASPs and crypto companies | Source: Fipto
4. Listings and Risk Controls: Well-regulated VASPs, especially in the EU under MiCA, apply stricter listing standards. They may require projects to provide a whitepaper, audited code, and risk disclosures before allowing a token to trade. While this sometimes means fewer speculative tokens are available compared to offshore exchanges, it reduces the risk of you buying into “fly-by-night” projects that disappear overnight.
Example Scenario: “Why did this token not list in the EU yet?”
Under MiCA, CASPs weigh disclosures and governance requirements before listing, so rollouts can be phased by region.
5. DeFi, NFTs, and Stablecoins - the Gray Zone for VASPs and Crypto Traders : Not all crypto activities neatly fit into the VASP category. Writing code alone doesn’t make someone a VASP, but if a person or company has real control or strong influence over a DeFi protocol,
NFT platform, or
stablecoin project, and actively facilitates services like trading, transfers, or custody, regulators may treat them as a VASP. This “functional approach” means classification depends on how the service operates in practice, not just what it calls itself.
Tip: Most trading delays or withdrawal issues happen at these touchpoints. Double-check deposit instructions, keep your KYC updated, and verify the destination wallet type (VASP vs. self-custody) before moving large amounts.
Top Tips for a Smoother Trading Experience on BingX
Trading is easier when you prepare for the compliance steps that VASPs must follow. Here are some simple ways to keep deposits and withdrawals running smoothly on BingX:
• Verify Early: Complete KYC before making large deposits or withdrawals. Pre-verification ensures you won’t get stuck waiting during high-demand events like token listings or airdrops.
• Whitelist and Label Addresses: Save frequently used wallet addresses in your BingX account and mark whether they belong to another exchange or VASP or your
self-custody wallet. This helps avoid errors and speeds up Travel Rule checks.
• Confirm Beneficiary Details: When sending funds to another exchange, always copy the exact account name or ID they provide. Mismatched details are one of the most common reasons withdrawals get delayed under the Travel Rule.
• Avoid Risky Sources: Don’t deposit coins that have passed through mixers or sanctioned wallets, as these can trigger extra compliance checks or even rejection. Use clean, traceable sources whenever possible.
• Keep Documents Handy: Have a valid ID, proof of address, and source-of-funds documents ready. Submitting them quickly can resolve reviews faster, especially during market volatility.
• Use Multiple Routes: If one blockchain network is congested or flagged, consider sending stablecoins or crypto over an alternative supported network. Having a backup option helps you move funds without delay.
Conclusion
VASPs are the bridge between crypto innovation and traditional financial rules. For everyday traders, this translates into standard processes like KYC, Travel Rule checks, and increasingly consistent protections under frameworks such as the EU’s MiCA. Preparing your documents in advance, double-checking transfer details, and understanding how regulations apply in your region can make trading smoother.
Still, remember that compliance reviews, cross-border transfers, and evolving rules can introduce delays or added checks. Staying informed and flexible helps you manage these risks while keeping your focus on trading opportunities.